Traumatic brain injury can cause long-lasting effects that seriously impact a patient’s quality of life. In the long term, the consequences of a traumatic brain injury could be life-changing. Dr. Jose Pizarro, a neuroradiologist based in Longboat Key, Florida, explains the long-term effects of traumatic brain injury and how neuroradiologists use diagnostic imaging to mitigate its impact.
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
A traumatic brain injury can result from a violent jolt to the body or a blow to the head. Any object that passes through brain tissue, such as a shattered piece of the skull or a bullet, can also cause traumatic brain injury.
Even a mild traumatic brain injury like a concussion can affect your brain cells and cause you to exhibit troubling mental and physical systems. More serious traumatic brain injuries can result in bleeding, torn tissues, bruising, and other physical damage. These severe injuries can cause long-term complications or death.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injuries
Physical symptoms of a mild traumatic brain injury include dizziness, a loss of balance, problems with speech, fatigue or drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, and headaches. Sensory symptoms can consist of smell and taste changes, ringing in the ears, and blurred vision. Cognitive symptoms can include a loss of consciousness, a dazed or confused state, memory problems, mood swings, depression, anxiety, and sleep problems.
A moderate to severe traumatic brain injury can have more wide-reaching and serious symptoms. All of the symptoms of a mild injury are possible in addition to these more serious symptoms.
A loss of consciousness lasting several minutes or hours is one of the most obvious symptoms. Patients may have a severe or worsening headache. They may experience nausea or repeated vomiting. They may have seizures. Their pupils may be dilated, and they may have clear fluid discharge from their ears or nose. They may be unable to awaken from sleep. They may have a loss of coordination or weakness in their fingers and toes.
Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injuries
The effects of moderate and severe traumatic brain injuries can be long-lasting and, in some cases, permanent. Rehabilitation and recovery are possible, but most people who have experienced a moderate to severe traumatic brain injury will have long-lasting impacts on their daily lives.
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries can cause permanent mental or physical disabilities. Even if patients appear to recover fully, they may have lingering problems that never go away.
People who have suffered moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries often find that working and completing tasks are extremely difficult. They may find that the abilities and skills they once exhibited are not as sharp as they were in the past.
Ongoing challenges related to a traumatic brain injury can also affect a patient’s personal life. People who have brain injuries may have difficulty navigating ordinary life tasks, including making changes at the grocery store or ordering in a restaurant. In some cases, traumatic brain injury patients are left entirely dependent on their caregivers.
Diagnostic Imaging
Neuroradiologists use diagnostic imaging to diagnose and treat the effects of traumatic brain injuries. Neuroradiologists are trained to interpret and use the results of diagnostic imaging tests to help patients recover functionality and some sense of a normal life.
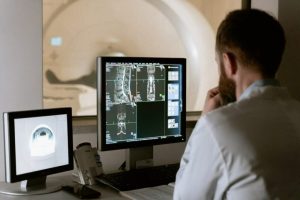
The first type of diagnostic imaging test used by a neuroradiologist is the CT scan or computed tomography scan. This scan produces internal images of the body. CT scans can generate pictures of soft tissues, bones, and organs in more detail than X-rays. CT scans can detect aneurysms, strokes, brain bleeds, brain tumors, and enlarged brain cavities.
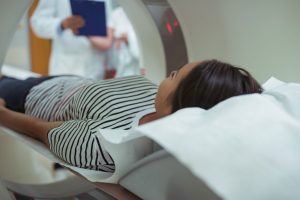
The next common diagnostic imaging test used by neuroradiologists is the MRI or magnetic resonance imaging scan. MRIs are used to take high-resolution photos of the inside of your body in multiple layers. This allows doctors to see exactly what is going on in different areas of the brain. Patients are placed in a large machine to receive the scan. The scan is painless though it can be challenging to sit still, and some patients have claustrophobia.
X-rays are the least sophisticated form of neuroradiology scans, but they can be highly useful nevertheless. X-rays take photos of brain and bone structures.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
Repeated and severe concussions can cause CTE or chronic traumatic encephalopathy. This brain disease is often found in football players. It can cause cognitive, emotional, and physical changes. It is also associated with severe mental issues, personality changes, and early-onset dementia.
Prognosis for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injury can have physical, cognitive, speech, sensory, emotional, and social impacts. It is highly important that any patient who has experienced an injury of this type see a neuroradiologist for help with their problems. Neuroradiologists like Dr. Jose Pizarro can use the newest and most advanced treatment methods to help their patients overcome the worst effects of traumatic brain injury and help them live more normal and fulfilling lives.